
Bt cotton area contraction drives regional pest resurgence, crop loss, and pesticide use Lu
The primary management tactic for lepidopteran pests of cotton in the United States of America (USA) is the use of transgenic cotton that produces Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Bt) toxins.The primary target pests of this technology are Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) and Heliothis virescens (F.) in the eastern and central Cotton Belt of the USA. Concerns over the evolution of resistance in H.

Bt cotton presentation12
The Story of Bt Cotton in India documents the process that it took for India's first genetically modified crop, Bt Cotton to be approved for commercialization. It captures the experiences of farmers and various stakeholders, particularly on how the technology has changed their lives and the challenges and opportunities they still face.
Biotechnology Agriculture
The approved resistance management plan for Bt maize in cotton production regions requires a structured refuge of non-Bt maize equal to 20% of the maize planted; that for Bt cotton relies on the.

National average cotton yields (Kgs/ha) before and after Bt cotton... Download Scientific Diagram
Production of Bt Cotton: As the share of Bt hybrids in the country's area sown under cotton touched 95%, average per-hectare lint yields more than doubled from 278 kg in 2000-01 to 566 kg in 2013-14. But both production and yields started falling after 2013-14, to 343.5 lakh bales and 447 kg/hectare in 2022-23..
Development of Bt. Cotton Download Scientific Diagram
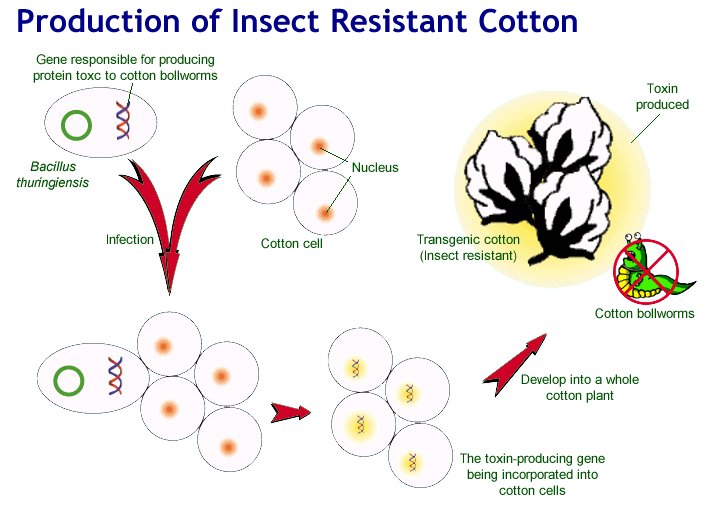
result is that Bt cotton has a built-in system that efficiently and consistently delivers Cry-toxins to the target pests from the time a newly hatched larva takes its first bite (fig. 1). Bt cotton offers a vastly improved method for delivering Cry-insecticides to target insects, compared to traditional Bt sprays. Bt cotton may

Percentage of cotton hectares planted with Bt cotton producing one... Download Scientific Diagram
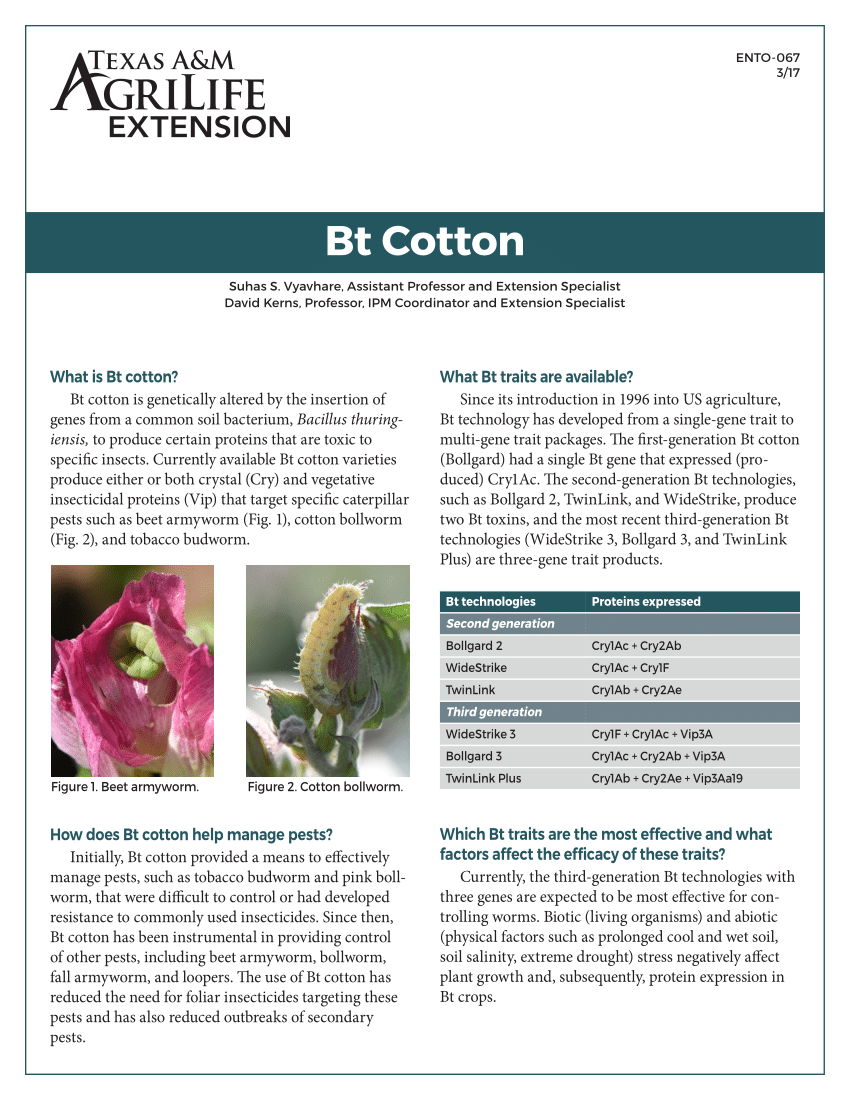
Bt Cotton Topics: Insects, Pests & Diseases Pesticides & Pest Management Plants & Crops Overview This 2-page publication explains how Bt cotton helps producers manage pests, what Bt traits are available, insect resistance to Bt, the need for scouting Bt cotton fields for caterpillar pests, and when to begin insecticide treatment.
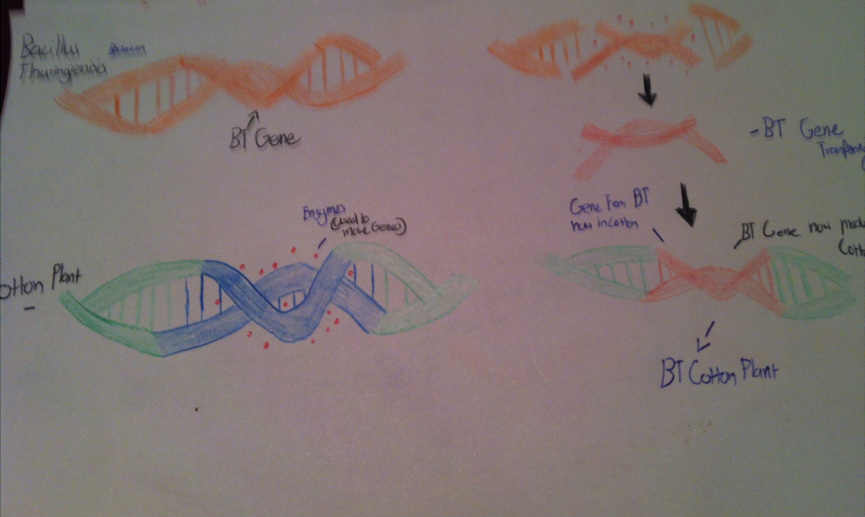
Diagram Explaining Bt Cotton Production Bt Cotton
Bt cotton is a genetically modified pest resistant plant cotton variety that produces an insecticide to combat bollworm . Description Strains of the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produce over 200 different Bt toxins, each harmful to different insects.

BT Cotton PDF Plant Breeding Modified Organism
Go to: Introduction The production of cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) plays an important role in the economy of many countries in tropical and subtropical regions of the world [ 1 ]. Arthropod pests have historically acted as major constraint on profitable cotton production and a limiting factor for the geographic expansion of the crop [ 1 ].

Bt crops production [17]. Download Scientific Diagram
The decision of the Genetic Engineering Approval committee (GEAC) of Government of India clearing the release of Bt cotton for commercial cultivation during 2002-2003 crop season, is considered as one of the major milestones in the history of cotton improvement in India.

How does Bt cotton kill bacteria?
4.2.2 Using Multiple Bt Genes for Bt Cotton. A theoretical model shows that Bt cotton containing two dissimilar Bt genes (pyramided plants) delays pest resistance to Bt significantly. Usually, Bt cotton with one single Bt gene can be used for 7-10 years before pests develop resistance to it; but for two Bt genes, it can be used for up to 20.

Science Behind the Bt Cotton Plasmid Gene
The fate of Bacillus thuringiensis ( Bt) cotton in India is one of the most closely-watched situations in the spread and impact of genetically modified (GM) crops. Intense interest in this one.
(PDF) Bt Cotton Fact Sheet
First-generation cotton, Bollgard, had only a single gene, while second-generation Bt crop, Bollgard II, TwinLink, and WideStrike had two genes. Most recent addition, the third-generation Bt crop comprises three genes, Bollgard III, WideStrike III, and TwinLink Plus. A timeline of Bt-cotton is given in Fig. 10.2.
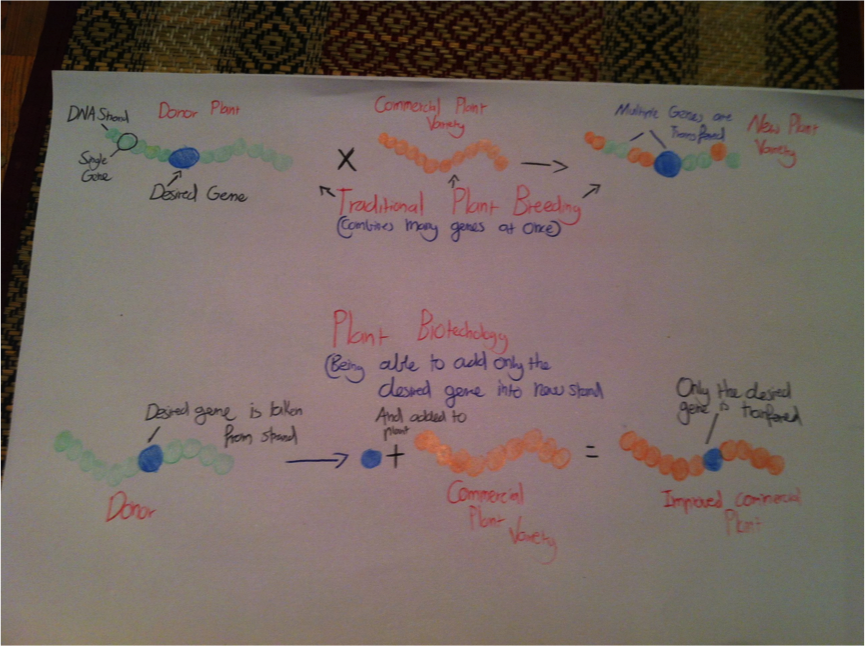
Diagram Explaining Bt Cotton Production Bt Cotton
"Bt cotton" plants dispatch an insecticide from a bacteria - Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) - that is toxic to the bollworm. The advantages of using Bt cotton over non-Bt varieties are.

Bt cotton yield and net incremental benefits Download Scientific Diagram
Bt toxins are highly specific. The toxins produced by Bt cotton and corn are toxic to a select number of arthropod species. Because cotton is primarily a fiber crop, the contamination of food with toxins from cotton is highly unlikely. However, extensive testing indicates a very low public health risk from the use, including ingestion, of food.

Transgenic plant ( B.T cotton) Biology diagrams, Science diagrams, Diagram
Download scientific diagram | Percentages of the total cotton area in Australia grown to Bt-cotton each year since its introduction in 1996. Ingardv was grown from 1996 to 2003 and Bollgard IIv.

Diffusion of Bt cotton in India, 2002 to 2011(Million hectares) Source... Download Scientific
Transgenic Bt cotton is the predominant commercial transgenic crop in China that has been cultivated for the longest period of time ( Lu et al., 2012 ). However, few studies have been conducted on assessing the fitness of GM cotton in some wild or semi-wild environments.